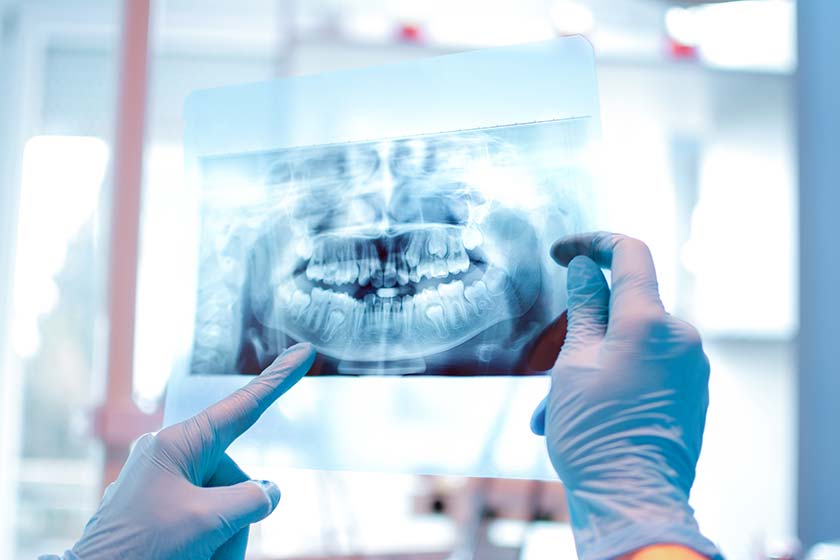
A panoramic dental x-ray is a radiological imaging method that uses X-rays to visualize the teeth, jaw, and oral tissues. Dental x-rays help diagnose various dental and gum issues, such as cavities, decay under fillings and crowns, bone loss, impacted teeth, cysts and tumors, infections, and abscesses. They also reveal problems that may not be visible during a regular examination.
The main concern with dental x-rays is radiation exposure. However, the amount of X-rays used in dental imaging is minimal. Panoramic x-ray machines are calibrated to low radiation levels, which have no adverse effects on health.
However, high doses or frequent x-rays could pose a risk, so it’s best to avoid unnecessary x-rays. In particular, it is recommended to avoid x-rays during pregnancy or other specific situations and consult a doctor beforehand. Patients with regular dental check-ups or frequent dental issues may require x-rays at specific intervals.
When considering radiation’s effects on the human body, it’s important to understand that the exposure dose and frequency matter most. The amount of radiation used in a dental x-ray is comparable to a portion of the natural radiation we encounter daily. For example, the radiation from a dental x-ray is similar to a fraction of the dose naturally received from sunlight.
These medical devices are crucial at the start of dental treatments, helping dentists gather detailed information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Modern digital dental x-ray machines are preferred for their ability to quickly transmit images and their low-radiation design, making them safe to use.


Leave A Comment